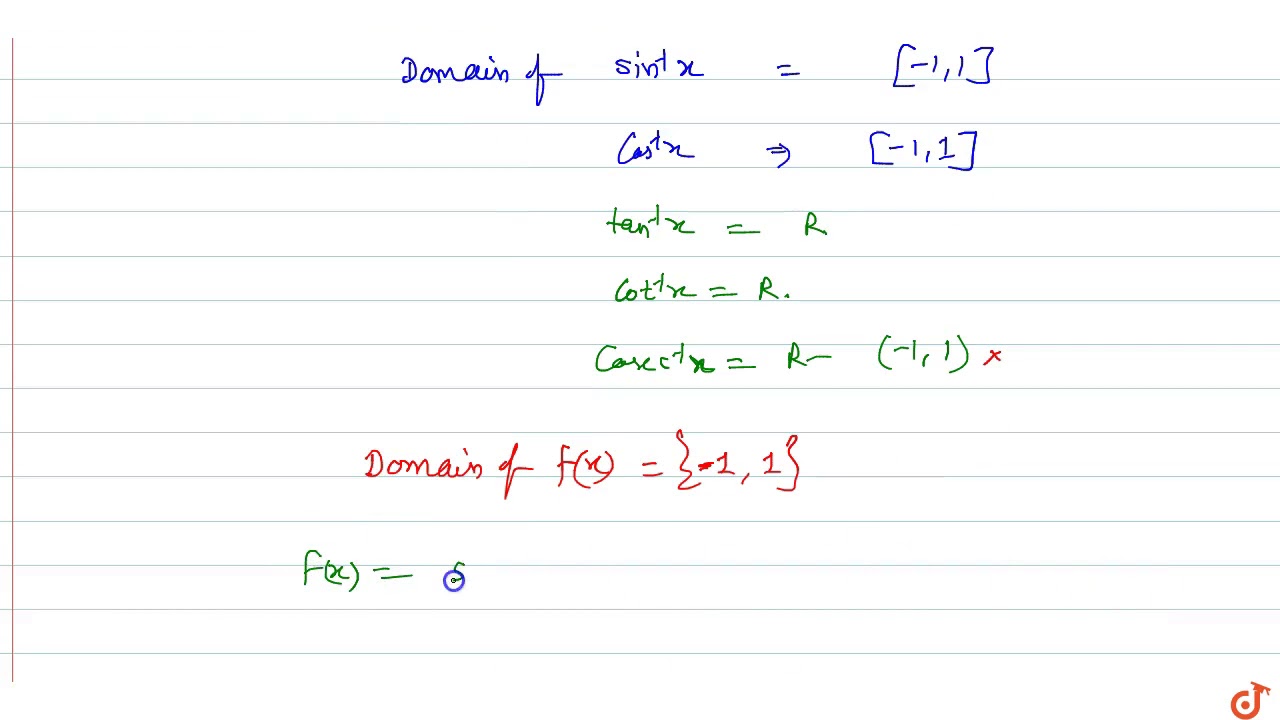
Domain (y1) = Range (y) More clearly, from the range of trigonometric functions, we can get the domain of inverse trigonometric functions It has been explained clearly below Domain of Inverse Trigonometric Functions Already we know the range of sin(x) That is, range of sin(x) is 1, 11 State the transformation for each function, and determine its domain and range a f(x) = sin(x 40°) b f(x) = sin x 8 2 3 Sketch f(x)=sin(x 90°)5 The graph of f(x) = sinx has been translated to the left 70°and up 6 units Write the new equation State the transformation for each sinusoidal function, and then sketch its graph 4//googl/JQ8NysDomain and Range of f(x,y) = arccos(x y) Multivariable Calculus

Find Domain And Range Of Sine Inverse 5x 1 Youtube
How to find domain for trigonometric functions
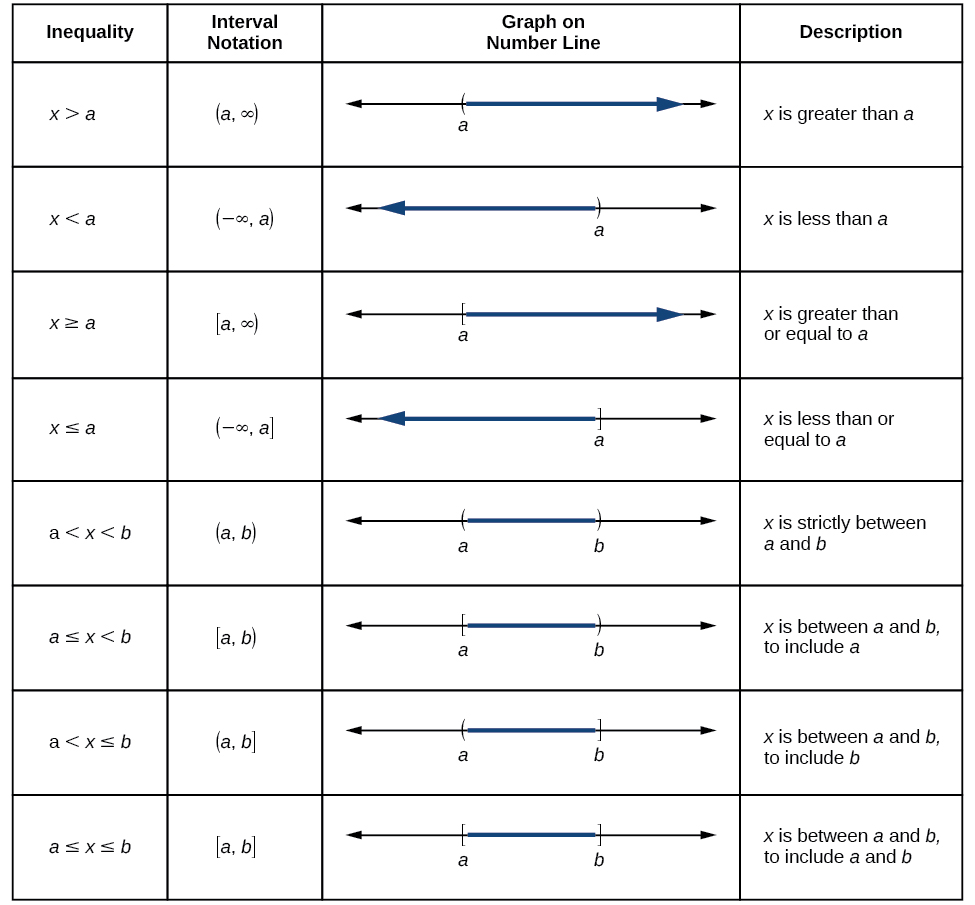
How to find domain for trigonometric functions-Find the Domain and Range f (x)=sin (x) f (x) = sin(x) f ( x) = sin ( x) The domain of the expression is all real numbers except where the expression is undefined In this case, there is no real number that makes the expression undefined Interval NotationHence, for the trigonometric functions f (x)= sin x and f (x)= cos x, the domain will consist of the entire set of real numbers, as they are defined for all the real numbers The range of f (x) = sin x and f (x)= cos x will lie from 1 to 1, including both 1 and 1, ie 1 ≤ sin x ≤1 1 ≤ cos x ≤1
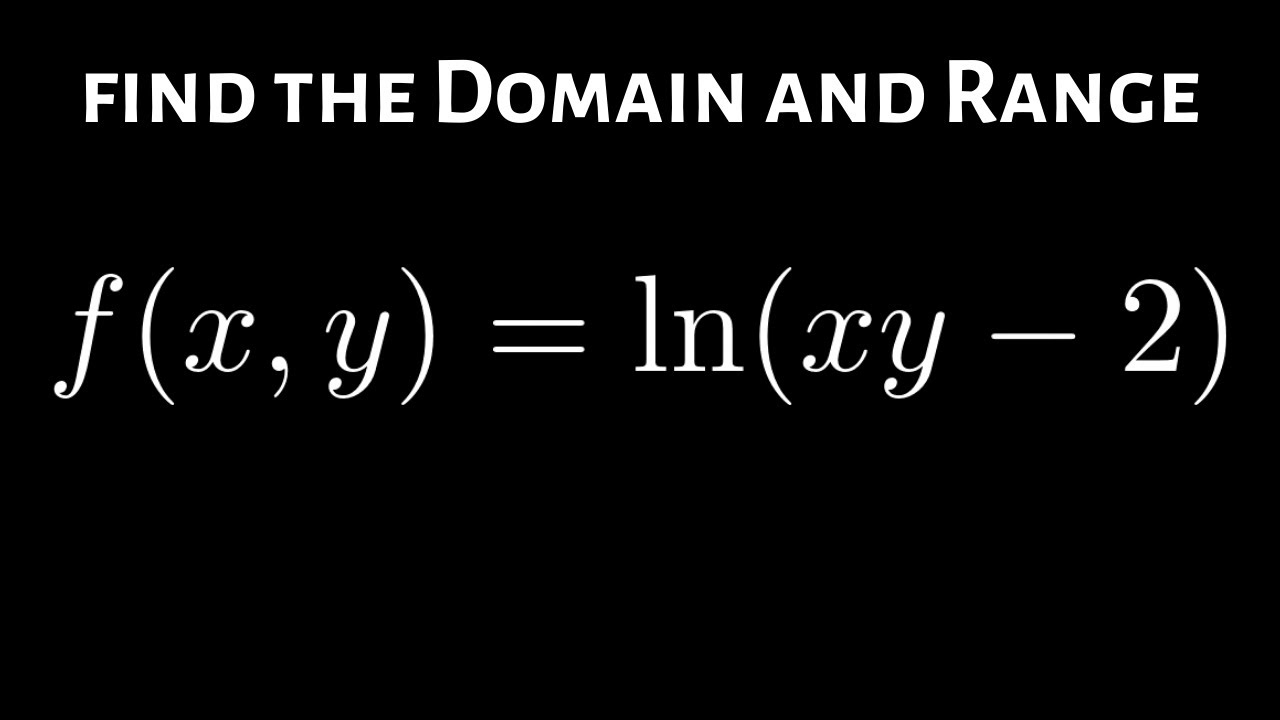



How To Find The Domain And Range Of F X Y Ln Xy 2 Youtube
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!!Apr 01, · Hello sir, Please explain this sum, Find the domain of the functions i) f (x) = 1/√ (x^2 5x 6) ii) f (x) = x^22x1/x^28x12 4x1 then x = mod (2x x)=4 where represent greatest integer function find domain of √x^25x6 Find range Find the range f (x)= root 9x^2 my doubt is that the answer says 0,3The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers f(x) such that f(x) ≤ 4 You can check that the vertex is indeed at (1, 4) Since a quadratic function has two mirror image halves, the line of reflection has to be in the middle of two points with the same y value
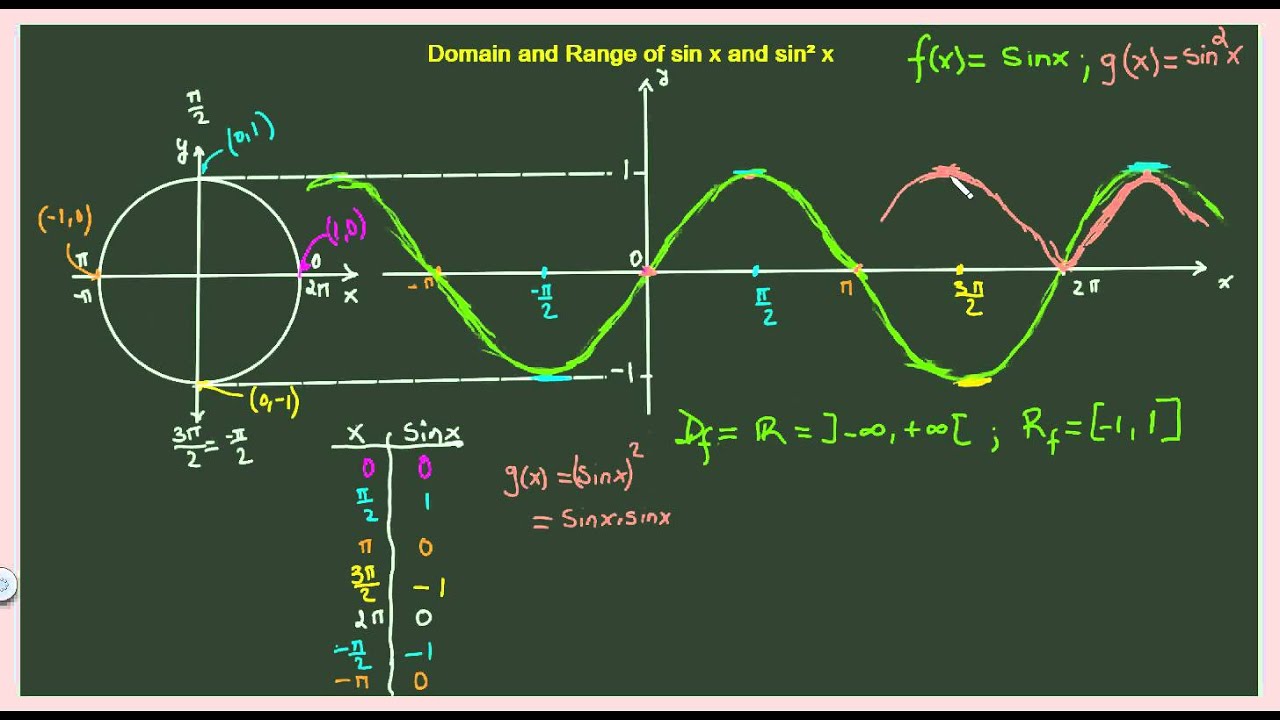
Where R is a set of all real numbers R {α, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, α} Range We know, (1) ≤ sin x ≤ (1) So, range is 1, 1 Codomain Any set of numbers (say, C) you may choose subject to the fact that Range is a subsetRational functions f(x) = 1/x have a domain of x ≠ 0 and a range of x ≠ 0 If you have a more complicated form, like f(x) = 1 / (x – 5), you can find the domain and range with the inverse function or a graph See Rational functions Sine functions and cosine functions have a domain of all real numbers and a range of 1 ≤ y ≤ 12 and Range(f) = 1;1 Hp 6,1 2L H5p 6,1 2Lpp 2 p 2 p1005 05 10 y=sinxp 2p 4 p 4 p 210
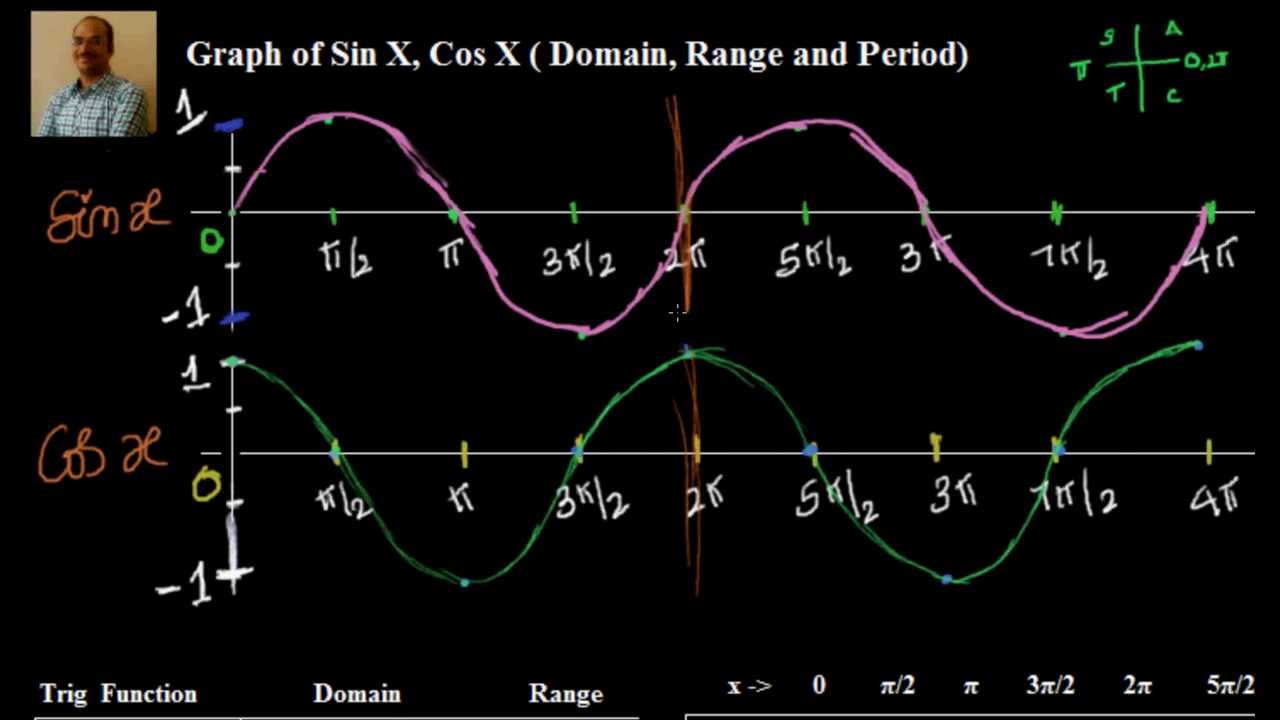
Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution Physics Mechanics domain\f(x)=\cos(2x5) domain\f(x)=\sin(3x) functiondomaincalculator domain f(x)=\frac{1}{xSin x, cos x, csc x, sec x, tan x, cot x In the above six trigonometric ratios, the first two trigonometric ratios sin x and cos x are defined for all real values of x The two trigonometric ratios sin x and cos x are defined for all real values of x So, the domain for sin x and cos x is all real numbers Range of sin x and cos xSine The graph is periodic and repeats every 2Π I think this function should be familiar Domain All real numbers R, also written as (–∞,∞)We can input any real number Range The output from the "sine" function box (I'm sorry, I really do think this way!) is restricted to numbers between –1 and 1, including both endpoints So it is –1,1



Domain And Range Of The Sin X And Sin X Function Video Dailymotion
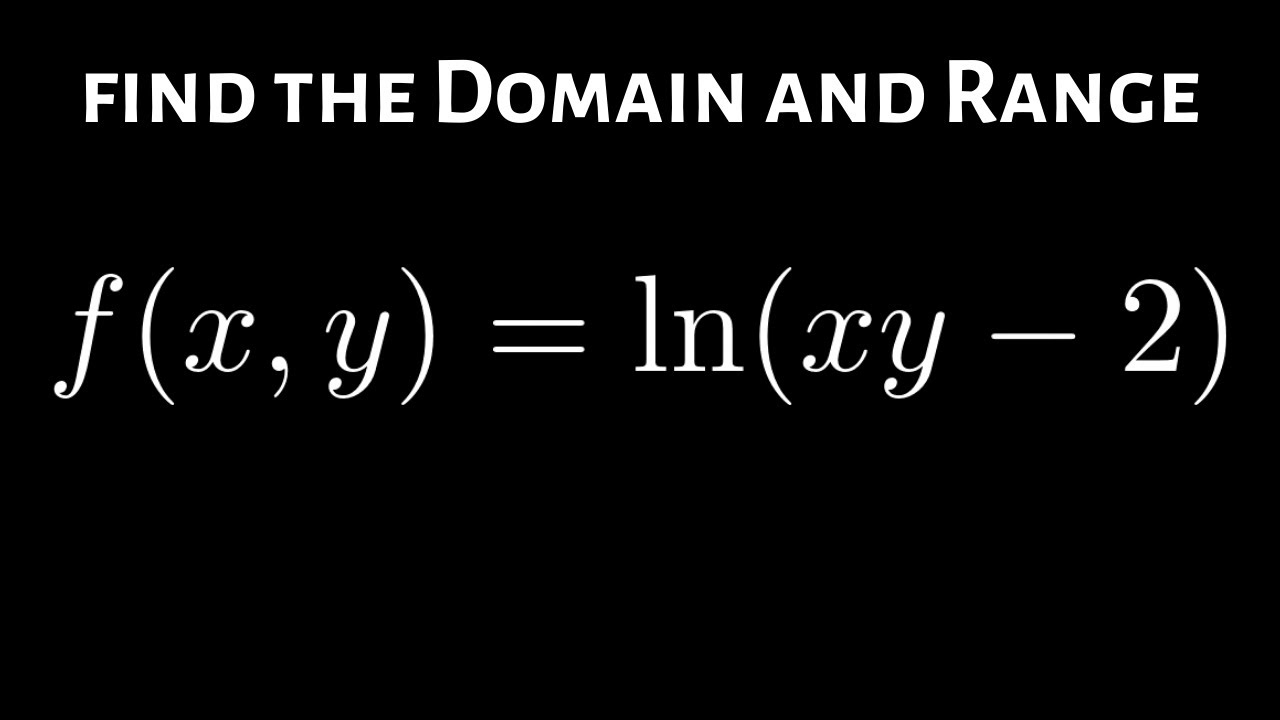



How To Find The Domain And Range Of F X Y Ln Xy 2 Youtube
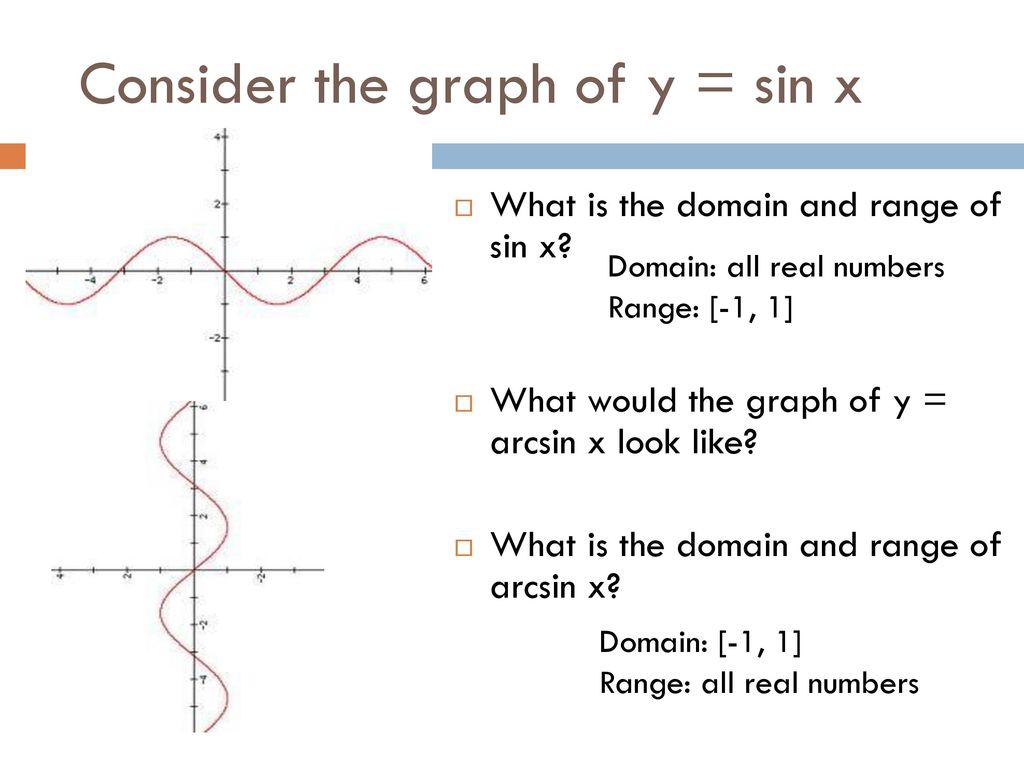
Find the domain and range of `f (x)=sqrt (cos (sin x))sin^1 ( (1x^2)/ (2x))` Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restartingQuestion Domain And Range (a) State The Domain And Range Of F(x) = Sin X (b) State The Domain And Range Of Y = Cos 0 (c) State The Domain And Range Of Y = Arcsin X (d) State The Domain And Range Of F(0) = Cos10 This problem has been solved!The graph of y=sin(x) is like a wave that forever oscillates between 1 and 1, in a shape that repeats itself every 2π units Specifically, this means that the domain of sin(x) is all real numbers, and the range is 1,1 See how we find the graph of y=sin(x) using the unitcircle definition of sin(x)




The Domain Of The Function F X Max Sin X Cos X Is Infty Infty The Range Of F X Is Youtube




Domain Range Of Functions Graphs Calculator Examples Cuemath
Calculus Find the Domain and Range f (x)= (sin (x))/x f (x) = sin (x) x f ( x) = sin ( x) x Set the denominator in sin(x) x sin ( x) x equal to 0 0 to find where the expression is undefined x = 0 x = 0 The domain is all values of x x that make the expression defined Interval NotationFind the domain and range of the function $$f(x) = \sqrt{x^2 25} $$ and $$ f(x) = \sqrt{25 x^2}$$Nov 08, 12 · The function f has a domain of 0,5and a range of 0,3 Start by sketching a potential graph of f Suppose the function k is defined as k(x)=f(x−3) Determine the domain and range of k Domain Range calcius Determine whether the relation represents a function




Inverses Of The Trigonometric Functions



Domain Range Of Functions Graphs Calculator Examples Cuemath
Jan 28, · All these are real values Here value of domain (x) can be any real number Hence, Domain = R (All real numbers) We note that that Range f (x) is 0 or negative numbers, Hence, Range = (−∞, 0 Ex 23, 2 Find the domain and range of the following real function (ii) f (x) = √ ( (9 −x^2)) It is given that the function is a real functionOct 02, 19 · when it comes to the domain, the denominator of the function has to be different from 0 so we look for those x who make the denominator zero and we take them away when it comes to the Range the sine fonction can take any small values which means that the fonction can take any value BUT 0Ikrammajid4 ikrammajid4 1806 Math Secondary School answered Find domain and range f(x)=1/32sinx 1 See answer ikrammajid4 is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn points SrijanShrivastava SrijanShrivastava For Domain;




Q5 Vii Ix X 9a X2 F X Log X 2 A X A 61 2 Find The Domain Range Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




Find Domain And Range Of Sine Inverse 5x 1 Youtube
Answer by venugopalramana (3286) ( Show Source ) You can put this solution on YOUR website!Domain, Range, and Period of the three main trigonometric functions 1 sin(x) Domain R = (1 ;1) Range 1;1 Period 2ˇ 2 cos(x) Domain R Range 1;1 Period 2ˇ 3 tan(x) Domain fxjx6= ˇ 2 kˇ, k= ;DOMAIN IS X>0 ALL REAL RANGE OF F (X) FOR THIS DOMAIN IS INFINITY TO INFINITY ALL REAL




What Is The Range Of Cos X




Notes On Exploring Sine And Cosine Graphs Learning Task
You can put this solution on YOUR website!F(x) = sin ( x ) (∞ , ∞) 1 , 1 f(x) = cos ( x ) (∞ , ∞)The set of all outputs of f is the range Example 1211 Understanding a function of two variables Let z = f(x, y) = x2 − y Evaluate f(1, 2), f(2, 1), and f( − 2, 4);
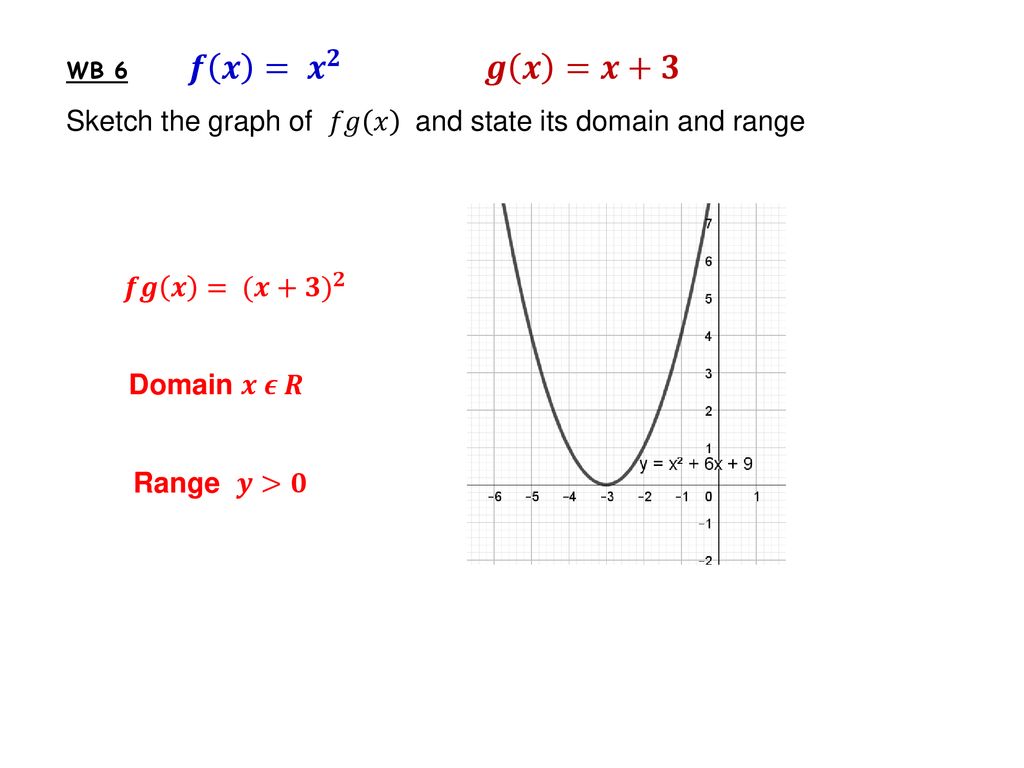



Functions Composite Ppt Download




Find The Domain Of Each Of The Following Functions F X Sin
6 rows · Domain Range ;In any inverse trigonometry function the argument within the inverse of sin has to be between 1 and 1 as these are the limits of sin function Range of inverse sin lies between pi/2 and pi/2For Cosine and Sine Functions, the Range and Domain There are no limitations on cosine and sine's domain functions So, their domain results in the form of x ∈ R It's important to note that, nonetheless, the range for y = cos (x) and y = sin (x) is between the range of (1 & 1)




4 Ways To Find The Range Of A Function Wikihow




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X Sin 1 X 2
Oct 19, 19 · Domain Domain of the function f(x) will be the intersection of domains of sinx and cosx As the domain of sinx as well as cosx is (∞,∞), thus the domain of the funtion f(x) will the the intersection of the two domains which comes out to be (∞,∞) that is, that x can take any real value ranging from ∞ to ∞Nov 09, 19 · Find the range of f(x) = sin^1x tan^1x cot^1x asked Nov 9, 19 in Sets, relations and functions by SumanMandal ( 546k points) inverse trigonometric functionsGiven, f(x) = sin1x tan1x sec1xClearly, the domain of f(x) is x = ± 1Thus, the range is {f(1), f( 1)}, ie π4, 3π4 Previous Year Papers Download Solved Question Papers Free for Offline Practice and view Solutions Online Test Series Take Zigya Full and Sectional Test Series Time it out for real assessment and get your results
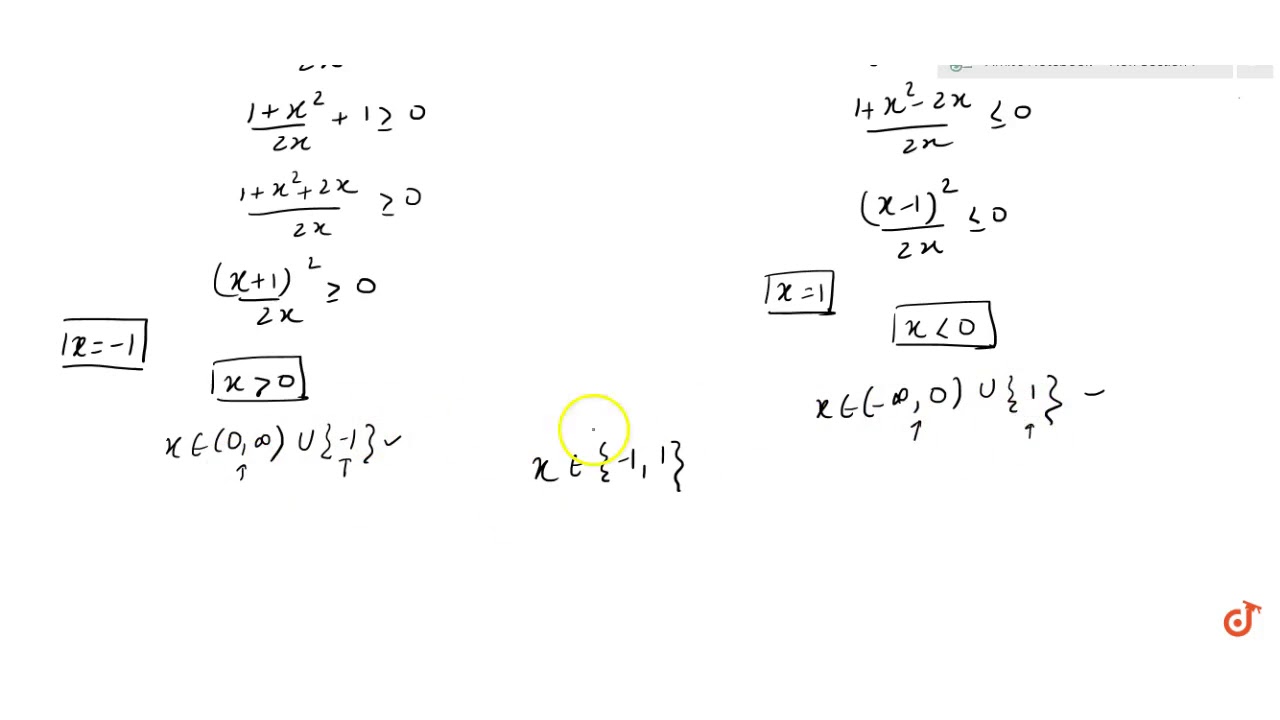



Find The Domain And Range Of F X Sqrt Cos Sin X Sin 1 1 X 2 2x Youtube




What Is The Domain And Range Of F X Cos X
May 27, 14 · find domain and range of the functions f x sin 1 5x f x 1 x 2 x 3 1 x 2 f x sinx x 2 5x 6 f x log to the base 2log to the base3 log to the base4 x f x MathematicsSep 10, · Find the range of the following functions given by f(x) = 1/(2 sin 3x)Sometimes integrals may have two singularities where they are improper Consider, for example, the function 1/((x 1) √ x) integrated from 0 to ∞ (shown right) At the lower bound, as x goes to 0 the function goes to ∞, and the upper bound is itself ∞, though the function goes to 0Thus this is a doubly improper integral




Topic 3 3 Domain And Range Of Trig And Inverse Trig Functions Trigonometry



Domain And Range Algebra And Trigonometry
Jun 18, · Find domain and range f(x)=1/32sinx Get the answers you need, now!Apr 29, 17 · Find the domain and the range of f (x)=2xsin x 1 See answer plus Add answer 5 pts report flag outlined bell outlined Log in to add comment trevoncoleman58 isDomain and range » Tips for entering queries Enter your queries using plain English To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary Here are some examples illustrating how to ask for the domain and range domain of log(x) (x^21)/(x^21) domain;




Solved 1 Consider The Function F X Y V X2 Y2 A S Chegg Com




Domain Of Advanced Functions Video Khan Academy
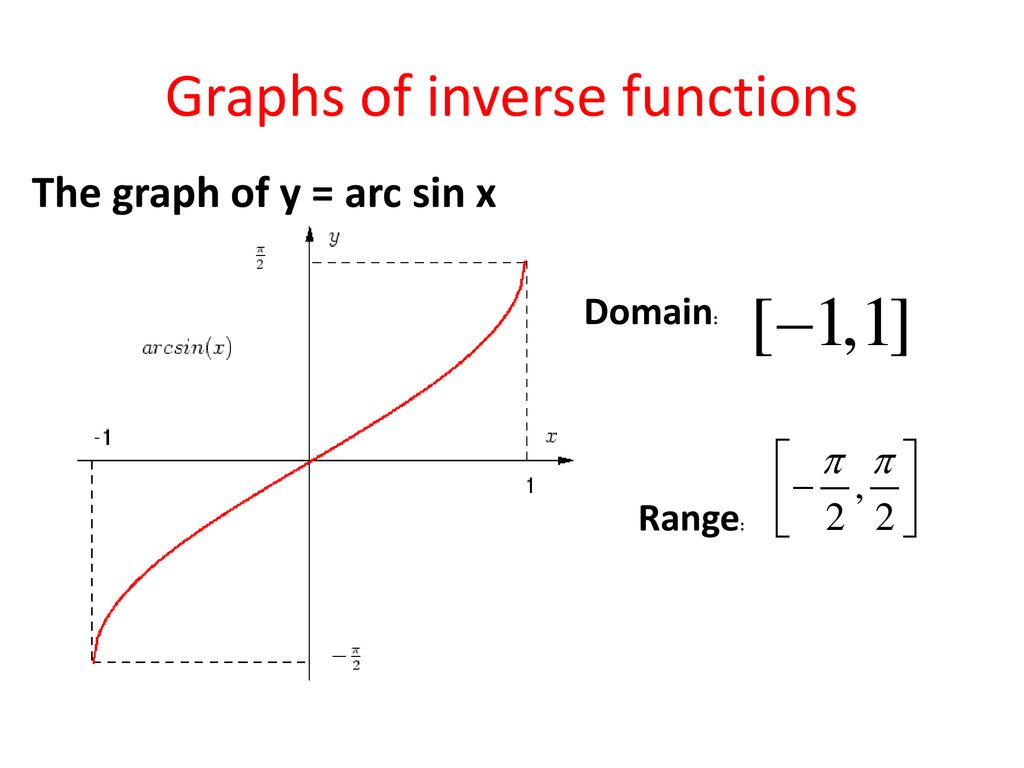
Find the domain and range of fAug 23, 15 · Explanation The sine function is repetitive and continuous and bounded between 3 and 3 and so since domain is all possible input x values, these are all real numbers, and since range is all possible output y values, these are all real numbers betweenDec 25, 17 · Explanation This video might help enter link description here Answer link Rhys Dec 25, 17 Domain −1 ≤ x ≤ 1 Range − π 2 ≤ y ≤ π 2




Find The Range Of F X Sin X Where Represents The Fractional Part Function And Youtube




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X Sin 1 1 E X
Click here to see ALL problems on logarithm Question 349 the range of f (x)=log2x is ?F(x) x f(x) = sin x We say that our function f(x) = sinx has domain −90 ≤ x ≤ 90 and that it has an inverse, f−1(x) = sin−1 x This inverse function is also written as arcsinx So, if the angle x lies in the range −90 ≤ x ≤ 90 and sinx = 3 4, we say x = sin−1(3 4) You can use your calculator to work out inverse sines Key PointIf f (x)=sin log (4−x2 /(1−x)) then the domain and range f are (respectively)



Answered Find The Inverse Function F Of The Bartleby




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X X 2 9 X 3
Nov 08, 19 · Find the domain and range of $f(x)=\sin^{1}(\sqrt{x^2x1})$ Finding the domain $$x^2x1>=0 \text { it is always true }$$ $$1May 01, 19 · Domain = (∞,∞) Range 0,∞) Stepbystep explanation To quickly solve this problem, we can use a graphing tool or a calculator to plot the equation Please see the attached image below, to find more information about the graph The equation is f(x)=2xsin(x) From the graph we can see that the domain is equal to all real numbersFind the domain and range of the function 1f(x)= 3sinx domain all real numbers (∞,∞) range 3,3 2f(x)= 2/x1 domain x≠1 (∞,1) U (1,∞)




Find The Domain And Range Of Each Of The Following Real Value Functions F X X 2 16




Solved Tt The Range Of The Function F X Sin X With Th Chegg Com
For f(x) = sin x Domain x Є R;Nov , 17 · Its domain and range can be found from the domain and range of sin(x) The csc( x ) cannot be defined for those values of x for which sin( x ) = 0 Its domain is all real numbers excluding x = 0The trigonometric function sin x is not onetoone functions, hence in order to create an inverse, we must restrict its domain The restricted sine function is given by f(x) = 8 < sin xˇ 2 ˇ 2 unde ned otherwise We have Domain(f) = ˇˇ 2;




Example 51 Consider F X Sin X G X Cos X Show That F And G




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X 1 Sqrt X 5
Y = sinx = sin(x 0) y = sin(x 1) y = sin(x 2) If we look at these changes in "c" we can see for y = sinx, c = 0 therefore the yaxis remains the same but when we look at y = sin(x 1) and y = sin(x 2) the values of "c" are 1 and 2 respectively Notice that a value of c = 1 meant a translation of the yaxis 1 unit to the left and aTAP THE ARROWS BELOW TO ADVANCE f(x)=cos(x) Domain and Range (infinity,infinity) 1,1Dec 29, · A function f of two variables is a rule that assigns each pair (x, y) in D a value z = f(x, y) in R D is the domain of f;



Sine Cosine Tangent Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
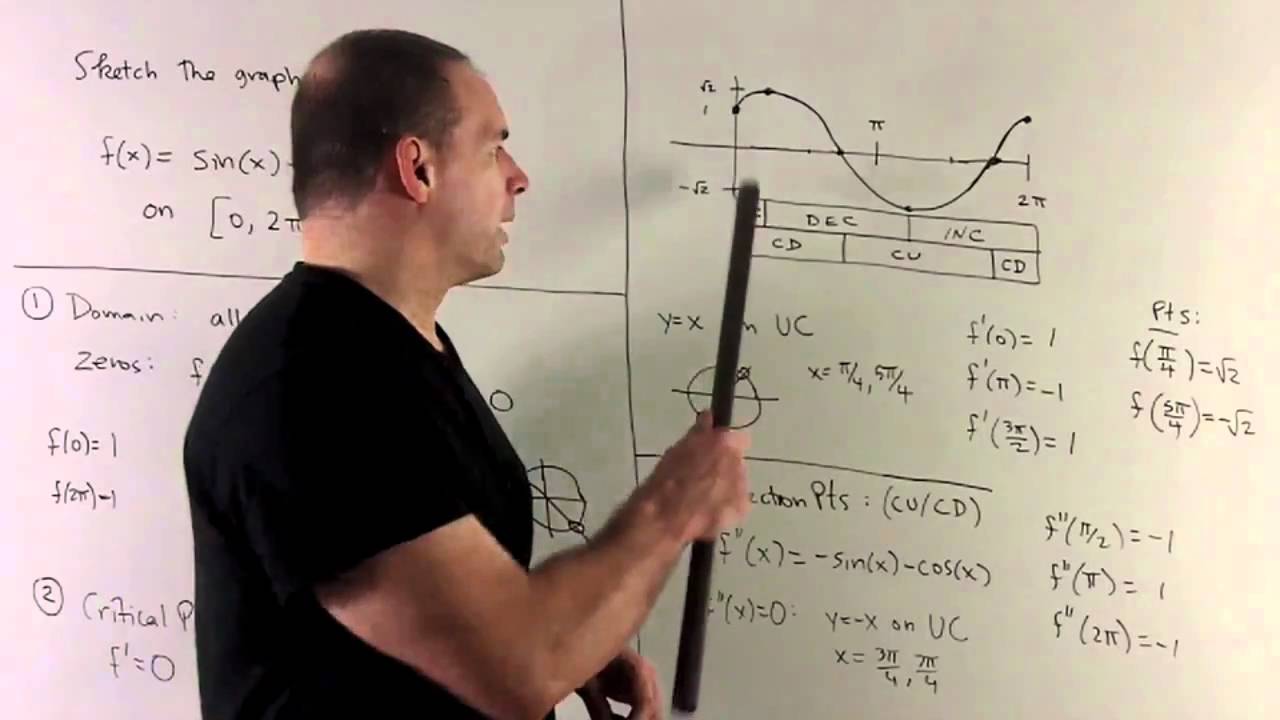



Graph Of F X Sin X Cos X Youtube
Y = (2−sin 3x)1 ( 1 )Let f (x) = (2−sin 3x)1 Domain of f (x) is (−∞, ∞)From ( 1 ),2−sin 3x= y1 ⇒ sin 3x= 2− y1 ⇒ sin 3x = y2y −1 ⇒ 3x =sin−1( y2y−1 )⇒ x = 31 sin−1( y2y−1 ) ∵ y = 2−sin 3x1 ∴ y > 0as −1 ≤sin 3x≤ 1 For x to be real−1 ≤ y2y−1 ≤1⇒ −y ≤ 2y−1≤ y y > 0 ⇒ 2y−1 ≥−y and 2y −1≤ y⇒ y ≥ 31 , y ≤ 1∴ Range of f (x) = 31 , 1See the answer Show transcribed image textJan 12, 15 · 1 note that f(0) = 1 and f is even so we only need to worry about the global minimum on 0 ≤ x < ∞ the critical numbers of f defined by f(x) = sinx x are given by f′(x) = xcosx − sinx x2 = 0 the positive critical numbers are the positive solutions xcosx − sinx = 0 which is equivalent to tanx = x this has a solution in (π, 3 / 2π




Finding The Domain And Range Of A Function Graphically Expii



Calculus Contents Paul Sutcliffe Office Cm212a Pdf Free Download
2;ˇ 2;3ˇ 2;g Range R Period ˇ Domain, Range, and De nition of the three main inverse trigonometric functionsFind the domain of 1/(e^(1/x)1) function domain square root of cos(x)




Find The Domain And Range Of The Inverse Of The Given Chegg Com




Find The Domain And Range Of The Following Functions I F X X 2 Ii F X X 1 3 X




2 Find Then Espai 1 Y Log 5 V2 Sinx Cos X 3 Find The




6 3 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
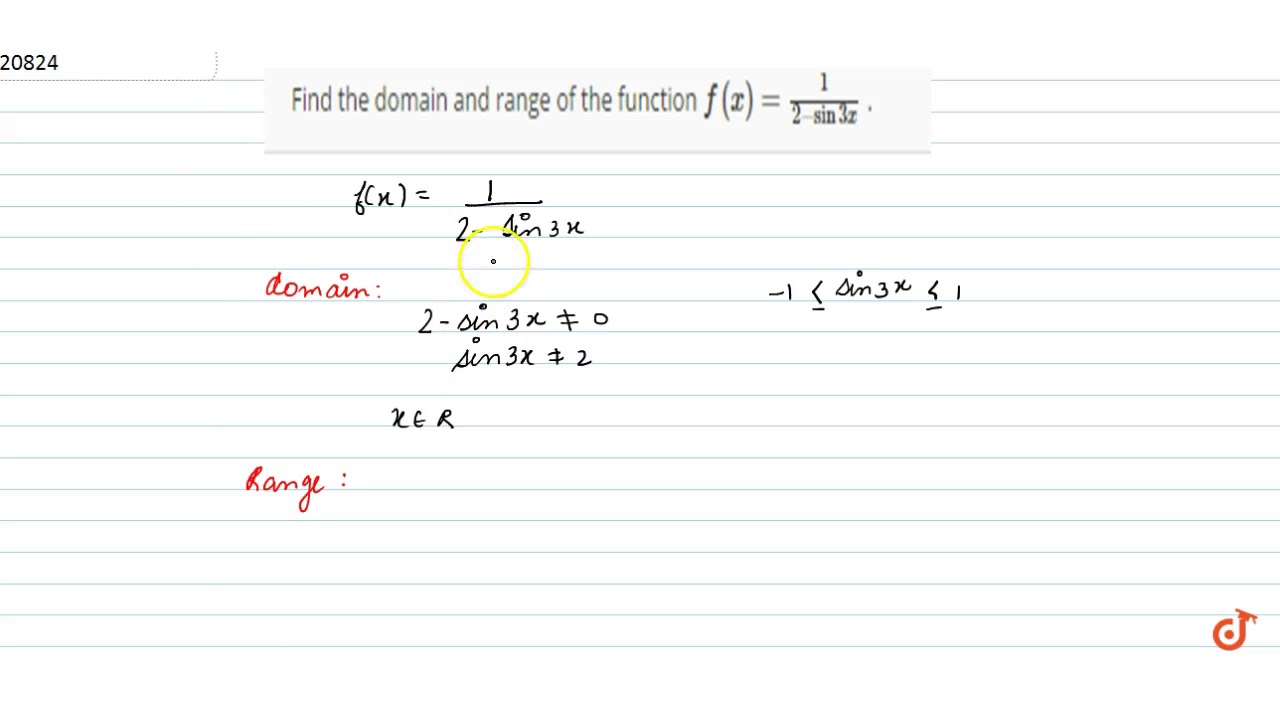



Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X 1 2 Sin3x Youtube




Restricting Domains Of Functions To Make Them Invertible Video Khan Academy
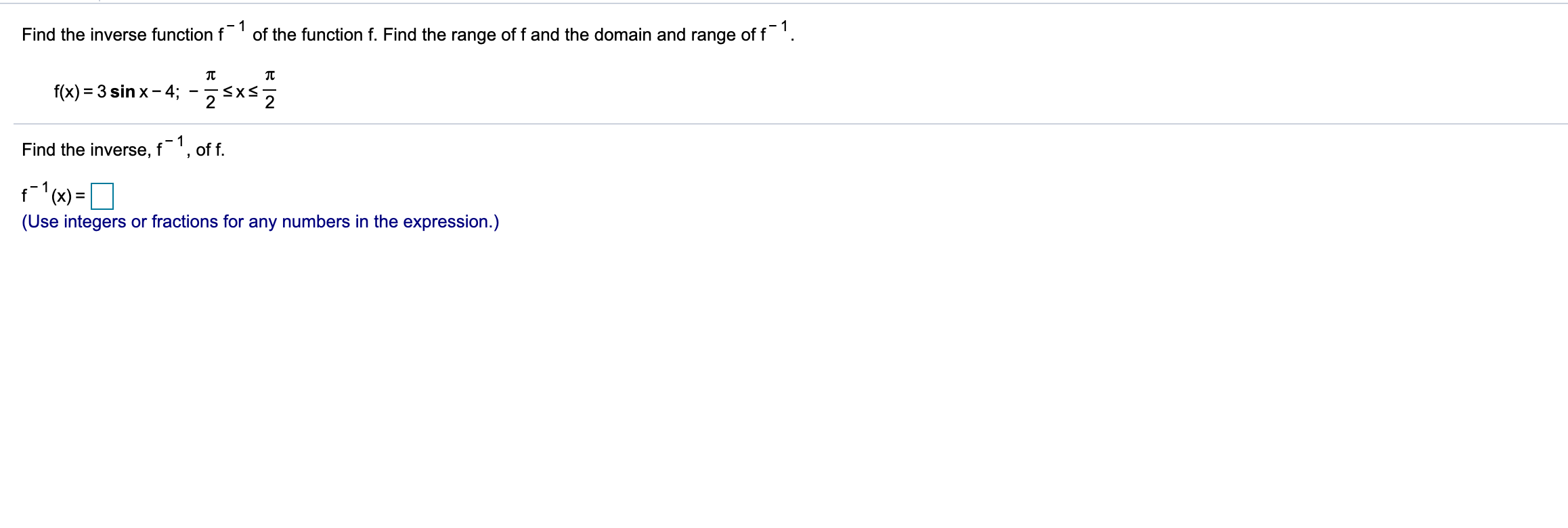



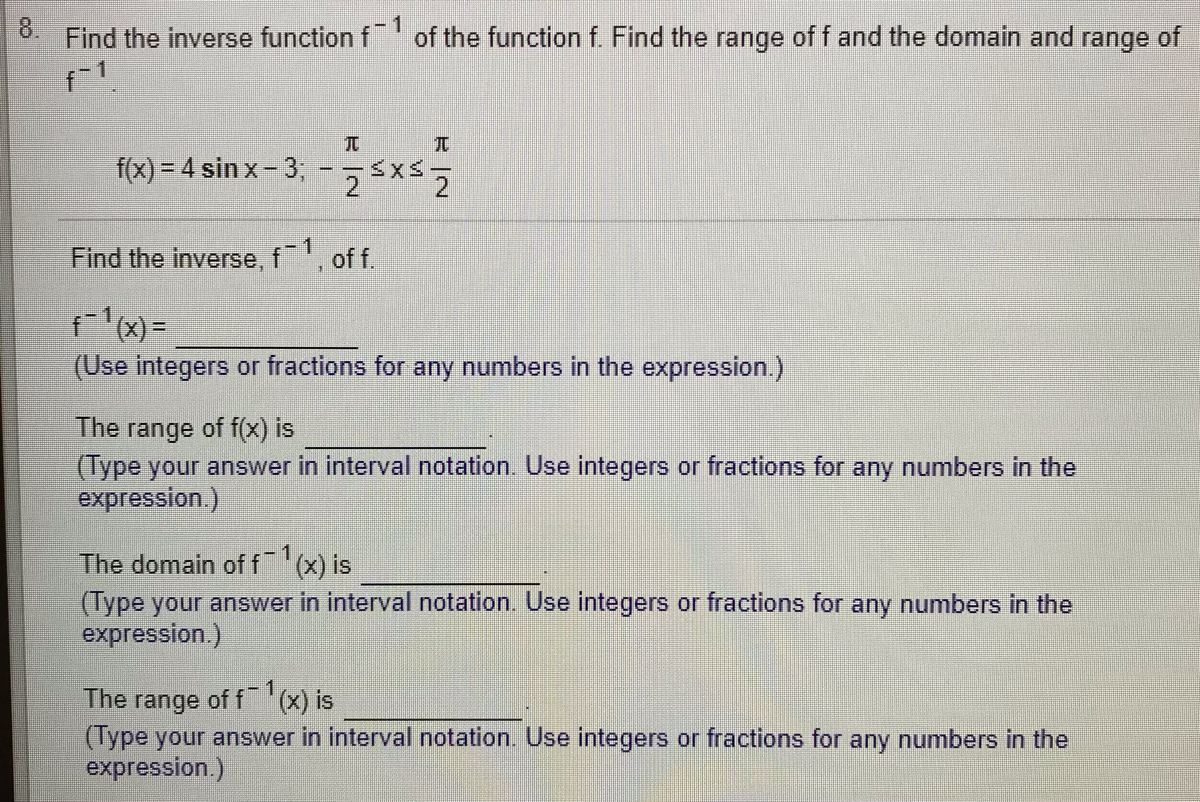
Solved Find The Inverse Function F 1 Of The Function F Chegg Com
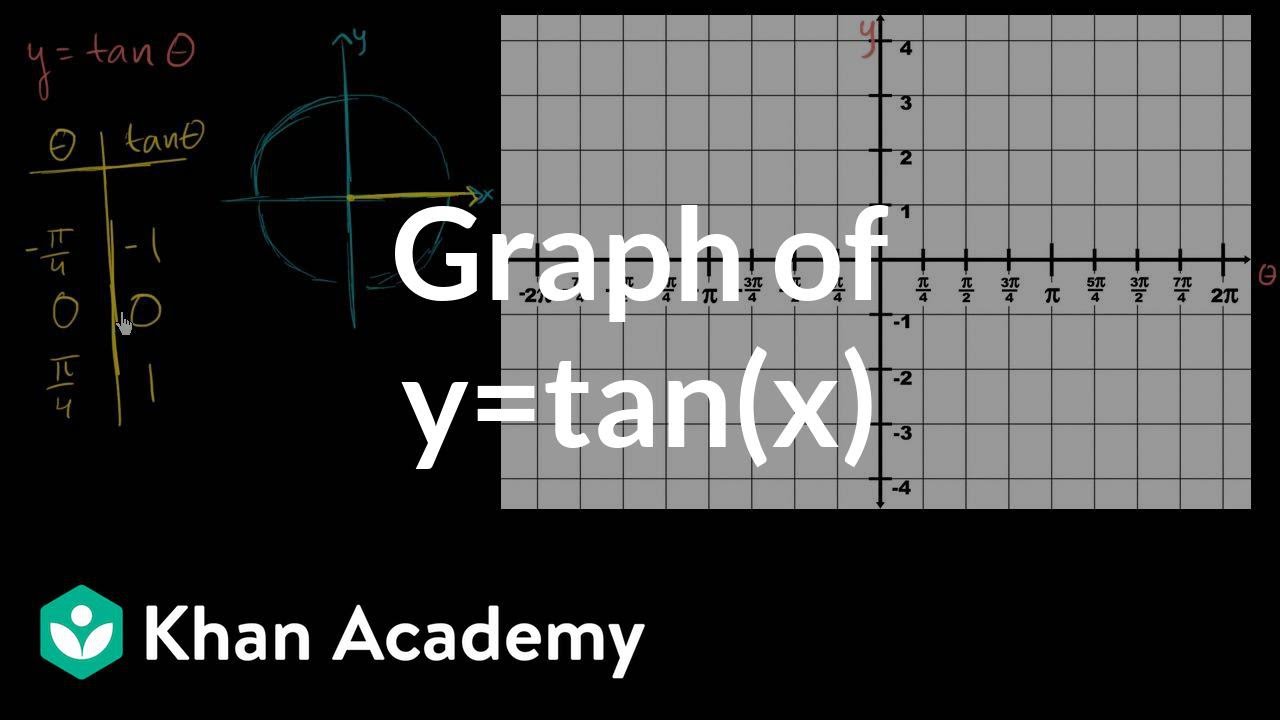



Graph Of Y Tan X Video Trigonometry Khan Academy




Find The Range Of Function F 0 1 Gt R F X X 3 X 2 4x 2sin 1x Youtube



Finding The Domain And Range Of A Function Graphically Expii




Domain Range Of Trigonometric Functions




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 2 Function Download Free Pdf




F X Find The Domain Range Of The Following Functie And As Greatest Inte Read The Symbols I Y Logs 12 Sinx Cosx 3
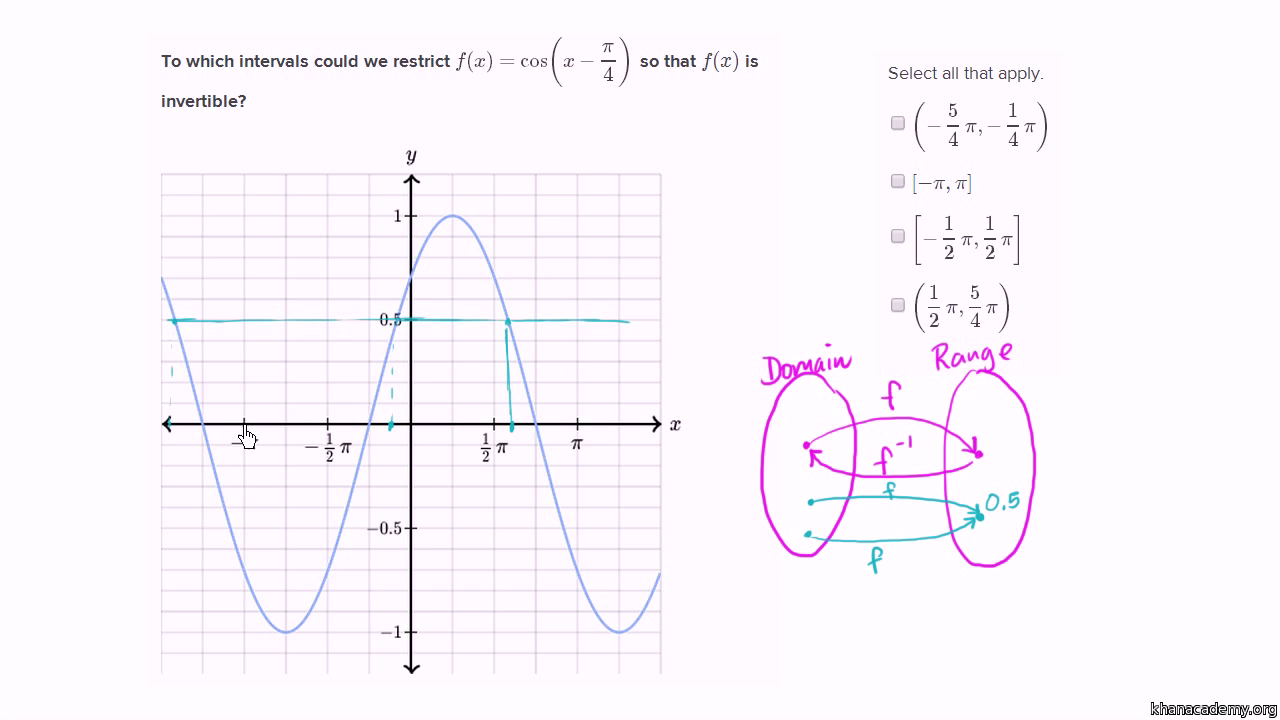



Restricting Domains Of Functions To Make Them Invertible Video Khan Academy




Find The Range Of Each Of The Following F X Ln Sin 1 X Youtube
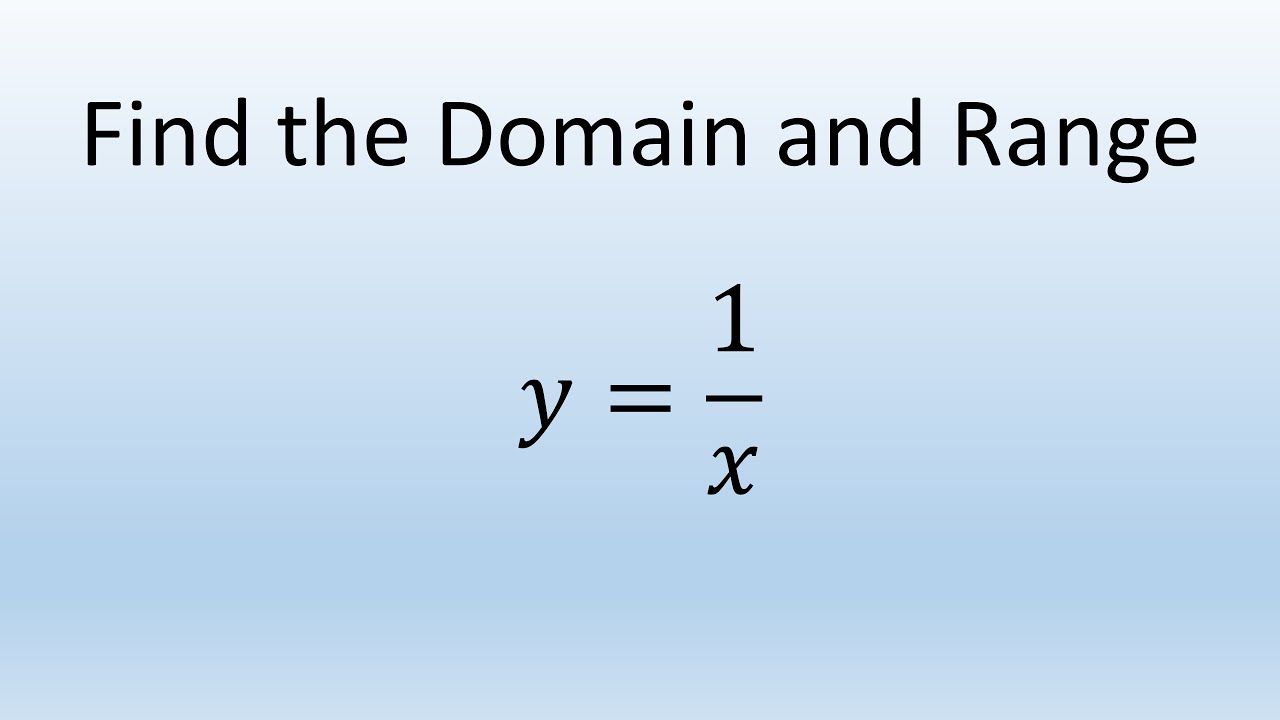



Find Domain And Range Of Function Y 1 X Youtube




Sine Wikipedia




Domain And Range Of Sin X And Its Inverse Youtube




Function Mathematics Wikipedia



Finding The Domain And Range Of A Function Graphically Expii




The Sum Of Integral Value Of The Elements In The Domain Of F X



2sinxcosx Graph Gamers Smart



The Domain And Range Of F X Sin 1x Cos 1 X Tan 1x Cot 1x Sec 1x Cosec 1x R Youtube



6 8 Trig Inverses And Their Graphs Ppt Download




Find Fog And Gof If F X Sinx G X X 2 Youtube




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 11 Chapter 3 Functions Download Free Pdf
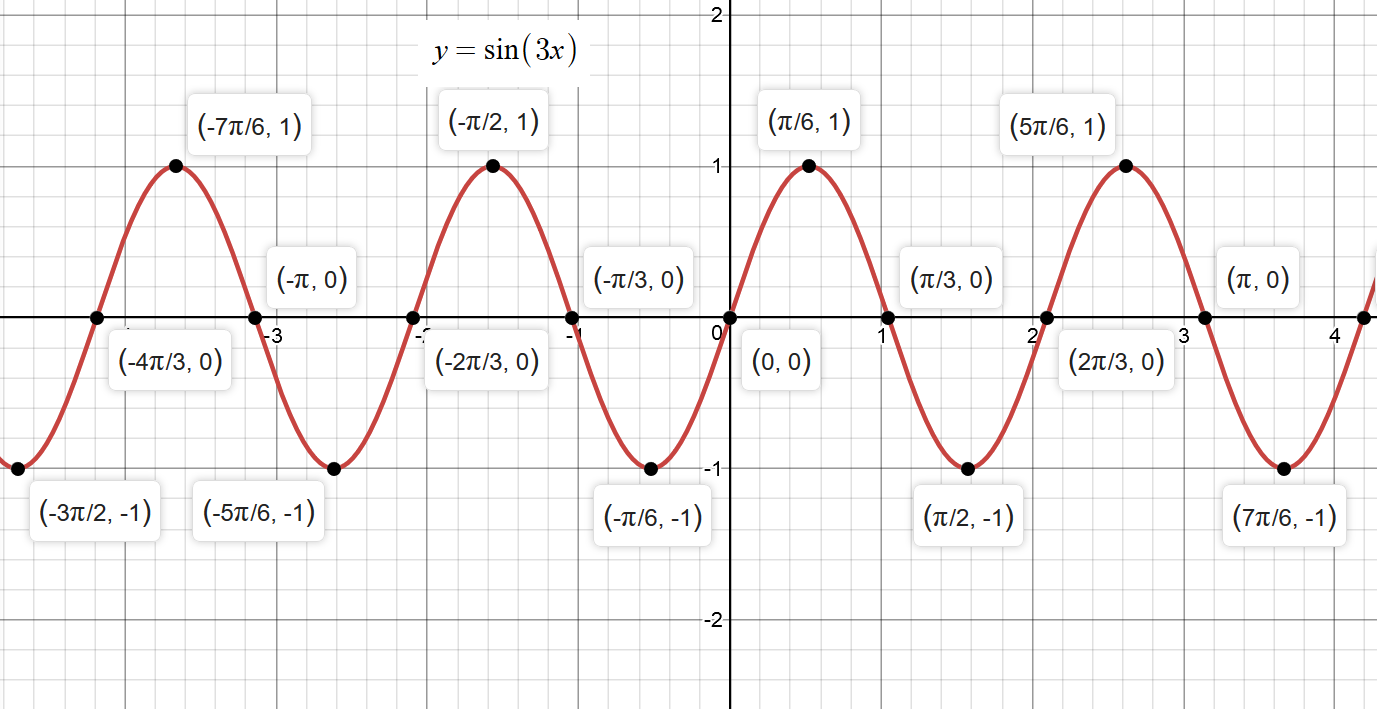



How Do You Graph Y Sin3x Socratic




6 8 Trig Inverses And Their Graphs Ppt Download




Calculating Range Of A Function Mathematics Stack Exchange
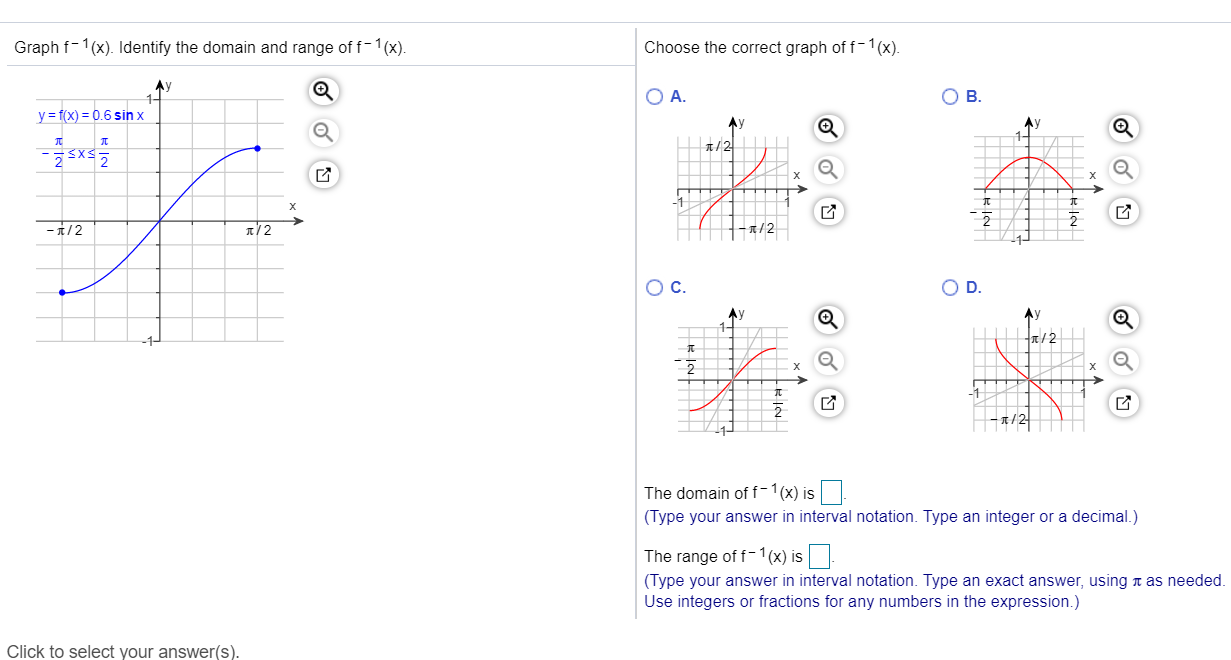



Solved Graph F 1 X Identify The Domain And Range Of F 1 Chegg Com




If F X Sin Log E Sqrt 4 X 2 1 X Then The Domain Of F




Find The Domain And The Range Of The Real Function F X X 3 X




F X X 4 4 X Find Domain And Range Brainly In




Find The Range Of F X 4sinx 3cosx Brainly In




Find The Domain And Range Of F X Sin 1 X X Where




The Number Of Integers In The Range Of Function F X Sinx C
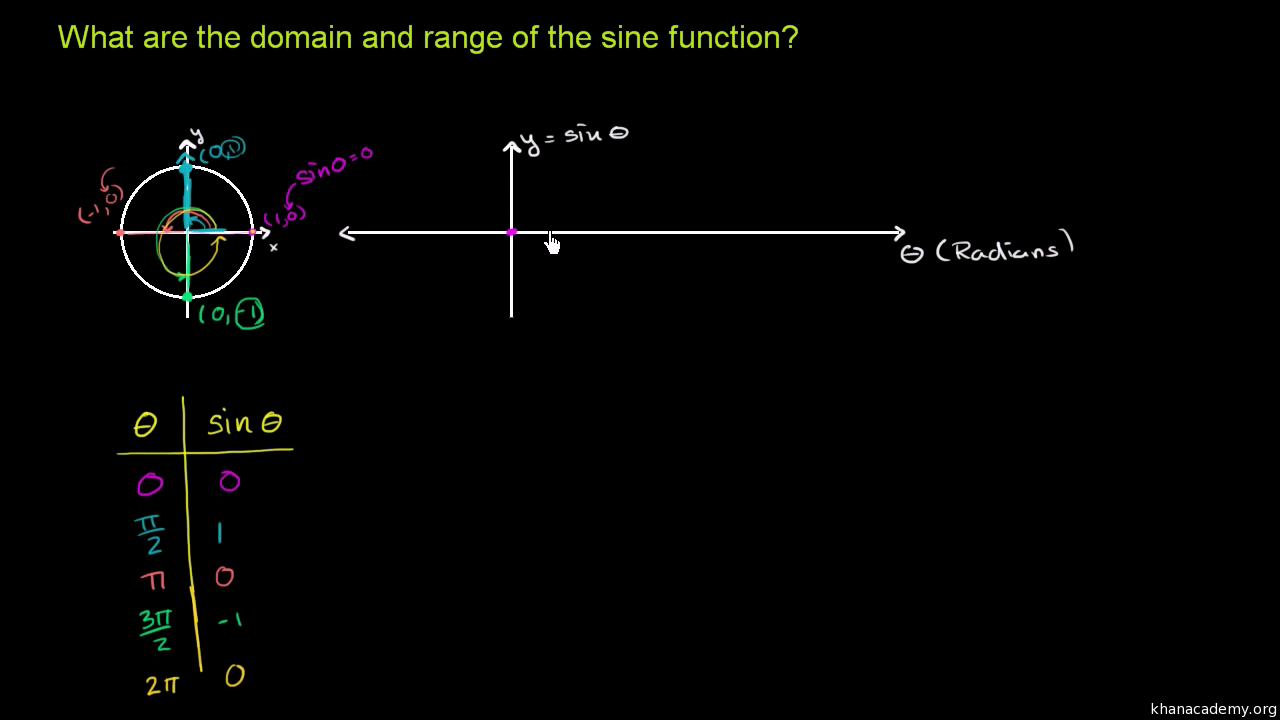



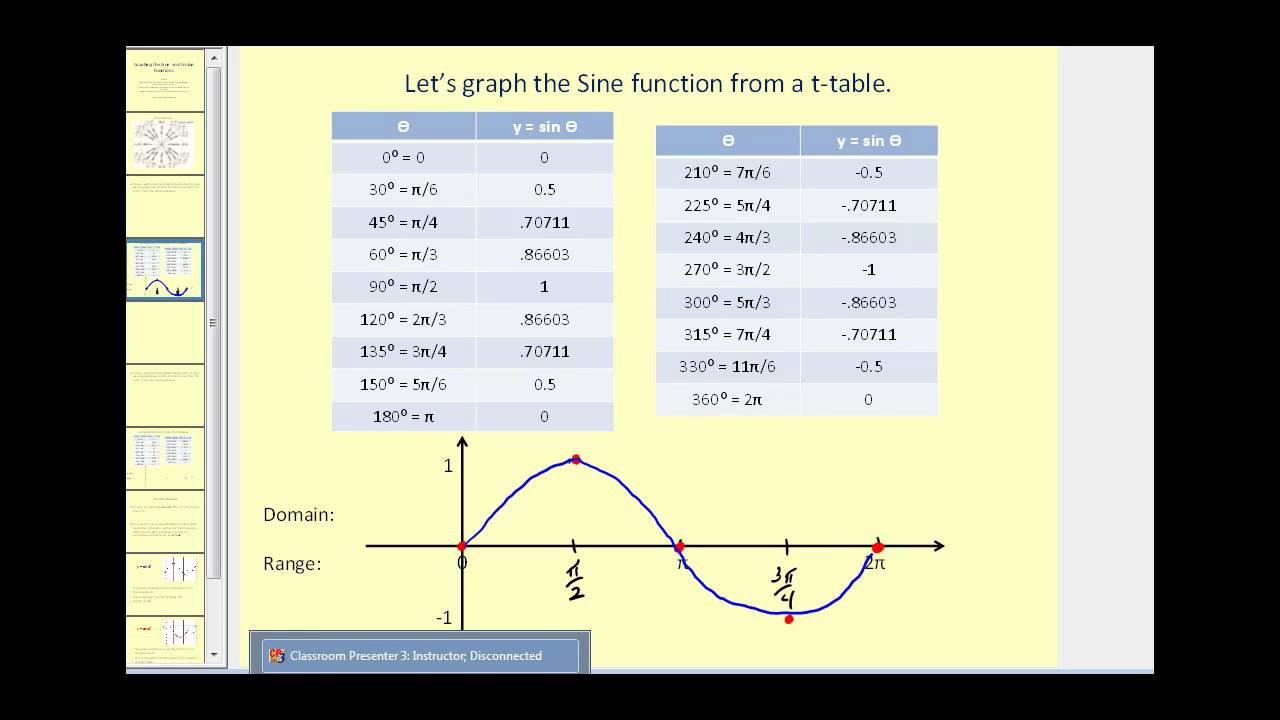
Graph Of Y Sin X Video Trigonometry Khan Academy




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X Sin X




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X 1 1 X 2 X I




What Is The Range Of A Function Expii




Domain Of A Function Wikipedia



Functions Inverse And Composite Functions
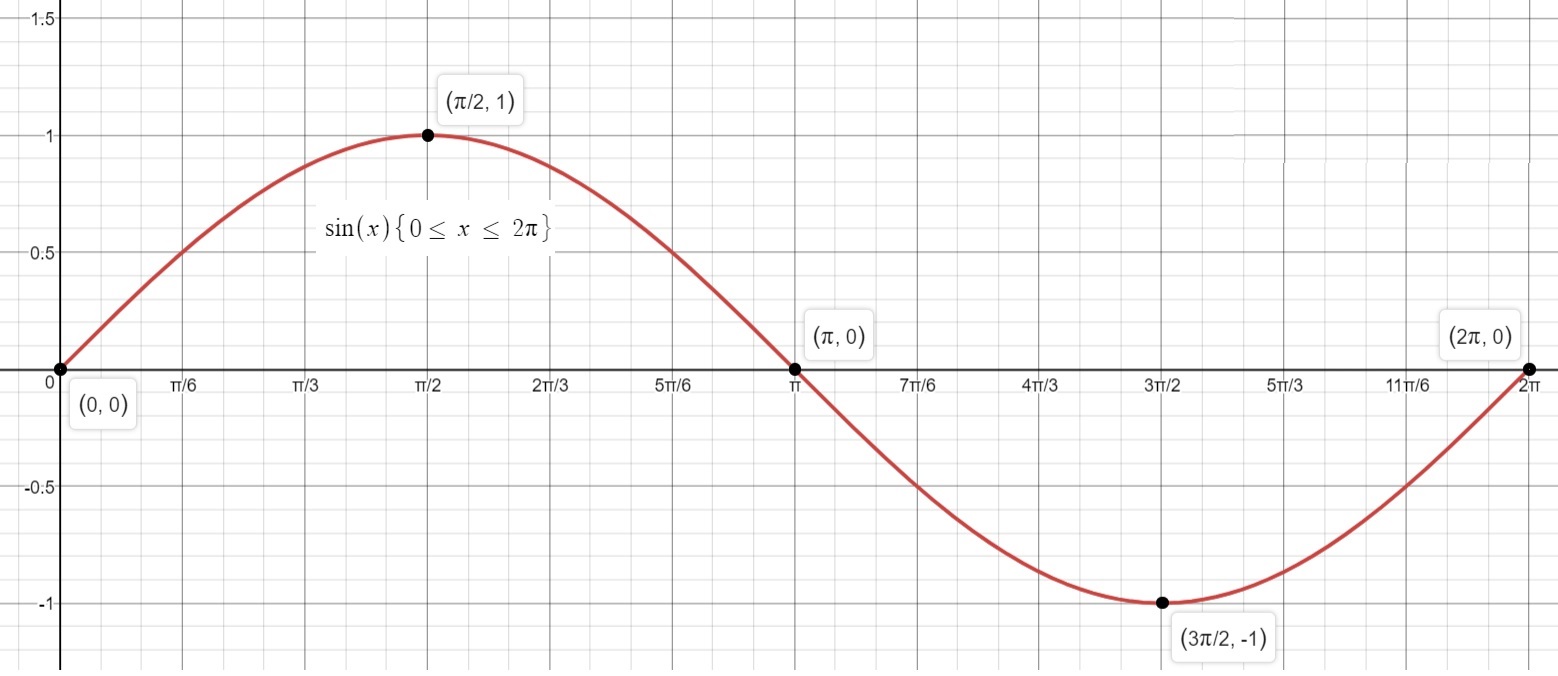



What Is The Domain And Range Of A Sine Graph Socratic



Trig Functions Domain And Range Of The Sin X And Sin X Function Youtube




Solved Find The Inverse Function F 1 Of The Function F F Chegg Com




Find The Domain And Range Of F X 1 Sin4x Cos4x Brainly In




Solved 10 Find The Domain And Range For The Indicated Fu Chegg Com




Domain Range Of Inverse Tangent Function Video Khan Academy




Match Cards In Pairs Then Try To Fill In Table Ppt Download



Inverse Trigonometric Functions Ppt Download




What Is The Range Of F X Cos X




Trig Sheet Sine Special Functions




The Range Of The Function F X 2 Sin X 3 Cos X Is




The Domain Of The Function F X 1 Sqrt Sinx Sinx Is
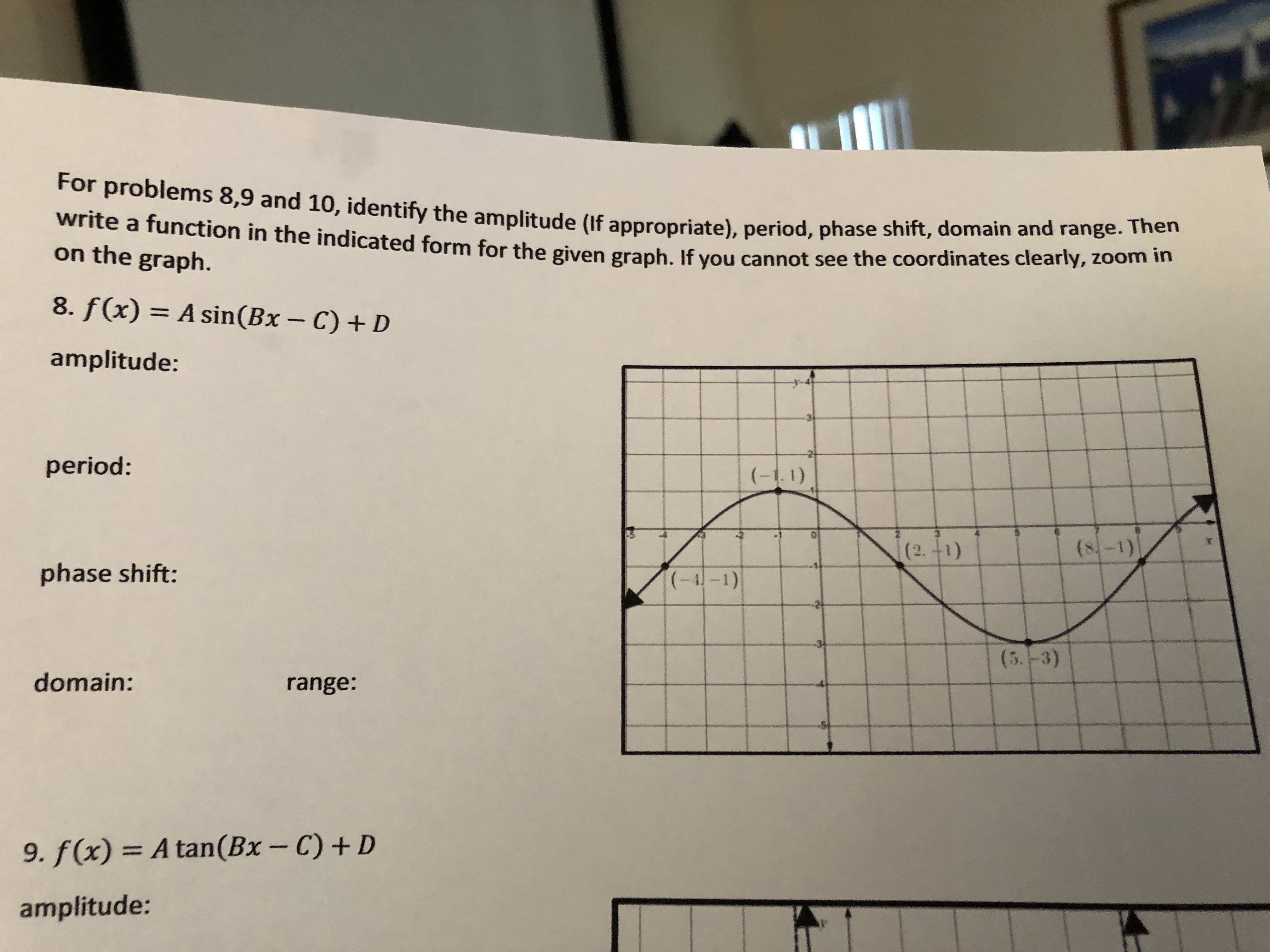



Answered 8 F X A Sin Bx C D 3d Bartleby



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿